Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease caused by a parasite that commonly infects a certain type of mosquito which feeds on humans. People who get malaria are typically very sick with high fevers, shaking chills, and flu-like illness. Although malaria can be a deadly disease, illness and death from malaria can usually be prevented.
About 1,500 cases of malaria are diagnosed in the United States each year. The vast majority of cases in the United States are in travelers and immigrants returning from countries where malaria transmission occurs, many from sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
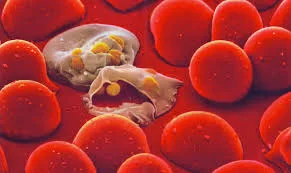
All the clinical symptoms associated with malaria are caused by the asexual erythrocytic or blood stage parasites. When the parasite develops in the erythrocyte, numerous known and unknown waste substances such as hemozoin pigment and other toxic factors accumulate in the infected red blood cell. These are dumped into the bloodstream when the infected cells lyse and release invasive merozoites. The hemozoin and other toxic factors such as glucose phosphate isomerase (GPI) stimulate macrophages and other cells to produce cytokines and other soluble factors which act to produce fever and rigors and probably influence other severe pathophysiology associated with malaria.
Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes, particularly those with mature trophozoites, adhere to the vascular endothelium of venular blood vessel walls and do not freely circulate in the blood. When this sequestration of infected erythrocytes occurs in the vessels of the brain it is believed to be a factor in causing the severe disease syndrome known as cerebral malaria, which is associated with high mortality.
What is malaria?
here are more than 100 types ofPlasmodium parasites, which can infect a variety of species. Scientists have identified five types that specifically infect humans, they are:
.
- falciparum - located worldwide in tropical and suburban areas, but predominately in Africa. An estimated 1 million people are killed by this strain every year. The strain can multiply rapidly and can adhere to blood vessel walls in the brain, causing rapid onset of severe malaria including cerebral malaria.
- P. vivax - located in Latin America, Africa, and Asia, it is arguably the most widespread due to the high population of Asia. This strain has a dormant liver stage that can activate and invade the blood after months or years, causing many patients to relapse.
- P. ovale - located mainly in West Africa, it is biologically and morphological very similar to P. vivax. However, unlike P. vivax, this strain can affect individuals who are negative with the Duffy blood group, which is the case for many residents of sub-Saharan Africa. This explains the greater prevalence of P. ovale (rather than P. vivax) in most of Africa.
- P. malariae - located worldwide and the only human malaria parasite to have a three-day cycle. If left untreated, P. malariae can cause a long-lasting, chronic infection that can last a lifetime and which may cause the Nephrotic syndrome.
- P. knowlesi - located in Southeast Asia and associated with macaques (a type of monkey). This strain has a 24 hour cycle and can, therefore, multiply rapidly once a patient is infected, causing an uncomplicated case to become serious very quickly. Fatal cases of infection with this strain have been reported.
Malaria is caused by the bites from the female Anopheles mosquito, which then infects the body with the parasite Plasmodium. This is the only mosquito that can cause malaria.
The successful development of the parasite within the mosquito depends on several factors, the most important being humidity and ambient temperatures.
When an infected mosquito bites a human host, the parasite enters the bloodstream and lays dormant within the liver. For the next 5-16 days, the host will show no symptoms but the malaria parasite will begin multiplying asexually.7
The new malaria parasites are then released back into the bloodstream when they infect red blood cells and again begin to multiply. Some malaria parasites, however, remain in the liver and are not released until later, resulting in recurrence.
An unaffected mosquito becomes infected once it feeds on an infected individual, thus beginning the cycle again.
Symptoms of malaria
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), malaria symptoms can be classified in two categories: uncomplicated and severe malaria.Uncomplicated malaria is diagnosed when symptoms are present, but there are no clinical or laboratory signs to indicate a severe infection or the dysfunction of vital organs. Individuals suffering from this form, can eventually develop severe malaria if the disease is left untreated, or if they have poor or no immunity to the disease.
Symptoms of uncomplicated malaria typically last 6-10 hours and occur in cycles that occur every second day, although some strains of the parasite can cause a longer cycle or mixed symptoms. Symptoms are often flu-like and may be undiagnosed or misdiagnosed in areas where malaria is less common. In areas where malaria is common, many patients recognize the symptoms as malaria and treat themselves without proper medical care.
Uncomplicated malaria typically has the following progression of symptoms through cold, hot and sweating stages:
- Sensation of cold, shivering
- Fever, headaches, and vomiting (seizures sometimes occur in young children)
- Sweats followed by a return to normal temperature, with tiredness.
- Fever and chills
- Impaired consciousness
- Prostration (adopting a prone or prayer position)
- Multiple convulsions
- Deep breathing and respiratory distress
- Abnormal bleeding and signs of anemia
- Clinical jaundice and evidence of vital organ dysfunction.
Text and Diagnosis
Treatment
- Which type of malaria parasite you have
- The severity of your symptoms
- Your age
- Whether you're pregnant
Medications
The most common antimalarial drugs include:
- Chloroquine (Aralen)
- Quinine sulfate (Qualaquin)
- Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)
- Mefloquine
- Combination of atovaquone and proguanil (Malarone).
The history of antimalarial medicine has been marked by a constant struggle between evolving drug-resistant parasites and the search for new drug formulations. In many parts of the world, for instance, resistance to chloroquine has rendered the drug ineffective.
- Chloroquine (Aralen)
- Quinine sulfate (Qualaquin)
- Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)
- Mefloquine
- Combination of atovaquone and proguanil (Malarone).
Prevention
In general, the drugs taken to prevent malaria are the same drugs used to treat the disease. Your doctor needs to know where you'll be traveling so that he or she can prescribe the drug that will work best on the type of malaria parasite most commonly found in that region.
No vaccine yet
Scientists around the world are trying to develop a safe and effective vaccine for malaria. As of yet, however, there is still no malaria vaccine approved for human use.
Reducing exposure to mosquitoes
In countries where malaria is common, prevention also involves keeping mosquitoes away from humans. Strategies include:
Reducing exposure to mosquitoes
In countries where malaria is common, prevention also involves keeping mosquitoes away from humans. Strategies include:
- Spraying your home. Treating your home's walls with insecticide can help kill adult mosquitoes that come inside.
- Sleeping under a net. Bed nets, particularly those treated with insecticide, are especially recommended for pregnant women and young children.
- Covering your skin. During active mosquito times, usually from dusk to dawn, wear pants and long-sleeved shirts.
- Spraying clothing and skin. Sprays containing permethrin are safe to use on clothing, while sprays containing DEET can be used on skin.









Informative post keep going dude.
ReplyDeleteI have been suffering from (HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS) disease for the past four years and had constant pain. During the first year, I had faith in God that i would be healed someday. This disease started circulating all over my body and i have been taking treatment from my doctor, few weeks ago i came on search on the internet if i could get any information concerning the prevention of this disease, on my search i saw a testimony of someone who has been healed from Herpes Simplex Virus and he also gave the email address of this man and advise anyone to contact him for any kind of problem that he would be of help, so i wrote to Dr Chukwu Madu herbal home telling him about my (Herpes Virus) he told me not to worry that i was going to be cured!! Though i never believed it,, well after all the procedures and remedy given to me by this man few weeks later i started experiencing changes all over me as the Dr Chukwu Madu assured me, after some time i went to my doctor to confirmed if i have be finally healed behold it was TRUE.., So friends if anyone have such problem and need help contact Doctor Chukwu Madu on. email
ReplyDelete(dr.chukwumaduherbalhome@gmail.com) OR WhatsApp him (+2347030936239)
1...HERPES CURE .
2...ALS CURE .
3..GET A JOB SPELL.
4.EPILEPSY .
5...PROMOTION IN THE OFFICE .
6...LOVE SPELL.
7...DIABETES CURE .
8...HIV CURE.
9...HPV CURE .
10>>EX BACK.
11... Kidney stone.
I started on COPD Herbal treatment from Ultimate Health Home, the treatment worked incredibly for my lungs condition. I used the herbal treatment for almost 4 months, it reversed my COPD. My severe shortness of breath, dry cough, chest tightness gradually disappeared. Reach Ultimate Health Home via their website at www.ultimatelifeclinic.com I can breath much better and It feels comfortable!
ReplyDelete